
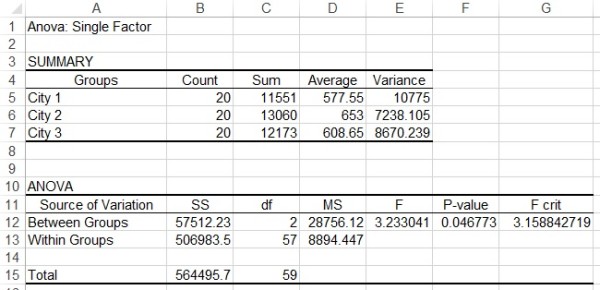
The actual sample size required to achieve 80% is 126. Actually, this sample size will be just short of 80% power (note that cell V16 is less than 80%). Rounding up we see that a sample size of 125 (cell V7) is required. Upon clicking on the OK button in the Goal Seek dialog box, you obtain the results shown in Figure 4.įigure 4 – Sample size required for a one-way ANOVA We can use Excel’s Goal Seek capability as shown in Figure 3.įigure 3 – Sample size for one-way ANOVA using Goal Seek Sample Size ExampleĮxample 2: How big a sample is required to achieve power of 80% for a one-way ANOVA with 4 groups and a Cohen’s effect size of.
The same result can be achieved using the formulas The calculation of the infinite sum for the noncentral F distribution stops when the level of precision is less than prec (default 0.000000001) or the number of terms in the infinite sum exceeds iter (default 1,000).įor Example 1, ANOVA1_POWER(Q11,Q9,Q10) =. 80) in a one-way ANOVA where type is as for ANOVA1_POWER except that type = 0 is not used. If type = 3 then f = (partial) eta-square effect size, while if type = 0 then f = the noncentrality parameter.ĪNOVA1_SIZE( f, k, 1− β, type, α, iter, prec) = the minimum sample size required to obtain power of at least 1− β (default. If type = 1 (default) then f = Cohen’s effect size, while if type = 2 then f = the RMSSE effect size.
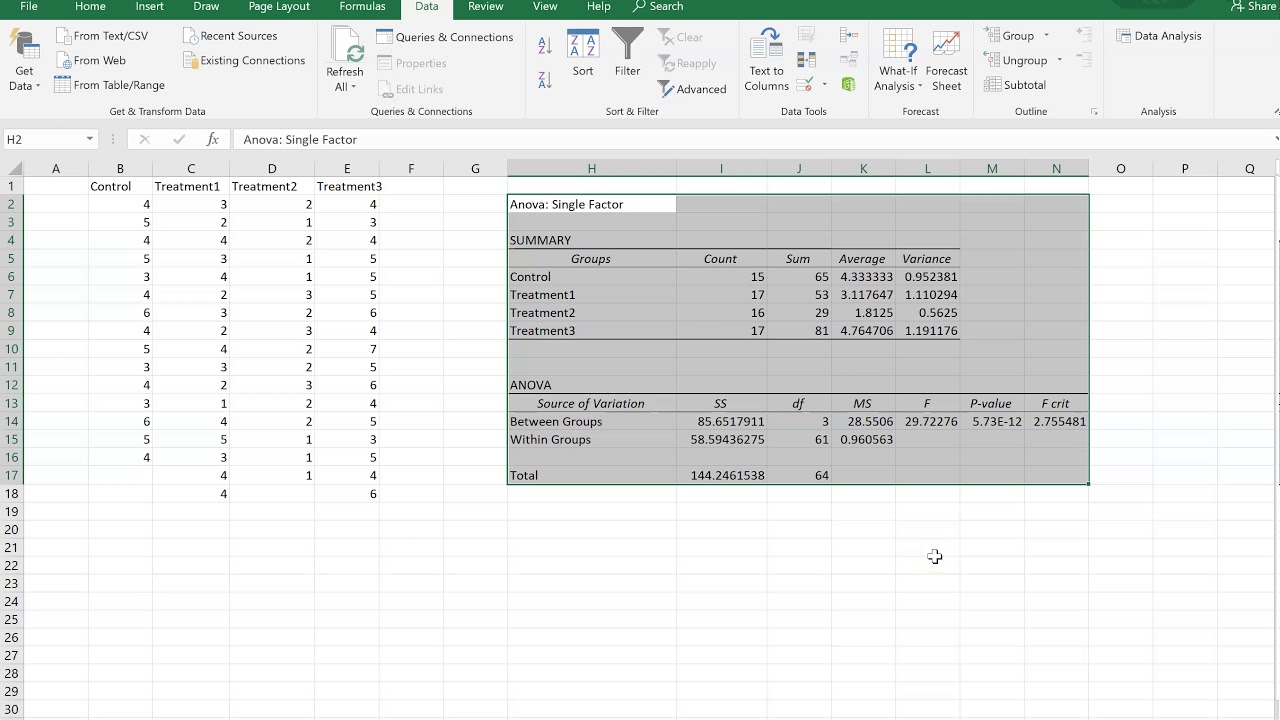
Real Statistics Functions: The Real Statistics Pack supplies the following two functions:ĪNOVA1_POWER( f, n, k, type, α, iter, prec) = the power of a one-way ANOVA where n = the sample size. We can achieve the same result using the first of the following two worksheet functions. Using the results in Figure 1, we now calculate the power in Figure 2. We start by showing the results of the one-way ANOVA using Real Statistics’s data analysis tool in Figure 1.
Power ExampleĮxample 1: Find the power for the test in Example 2 of One-way ANOVA Basic Concepts. The noncentrality parameter is also equal to f 2n where f is the effect size measure described in Effect Size for ANOVA. To calculate the power of a one-way ANOVA, we use the noncentral F distribution F( df B, df E, λ) where the noncentrality parameter is


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
